
IE decreases down a group from top to bottom.This is because since electrons are pulled closer to nucleus (see atomic radius), more difficult to remove them. IE increases across period from left to right.Positive sign meaning energy used (endothermic).Second ionization energy IE 2 is energy required to remove electron from IE 1.First ionization energy IE 1 relates to process:.The minimum energy required to remove 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of neutral gaseous atoms in ground-state.This is because the extra electron in the anion results in greater repulsion between valence electrons, thus larger radius. This is because there are more protons than electrons in the cation, so valence are more strongly attracted to nucleus. Radii of cations and anions are different from parent atoms.Distance from center to the outer most region in ion.Each new period begins with new energy level which is farther from nucleus, increasing atomic radius. Atomic radius increase down group from top to bottom.Nucleus’s positive charge is greater relative to charge of electrons in same shell, pulling electrons closer to nucleus and thus reducing atomic radius Atomic radius decreases across period from left to right.Way of finding radius would be to measure distance between two atoms in diatomic molecule X 2 and divide by two for the radius.Bohr model has orbits, thus radius can be measured easily however we know that this is highly simplistic.Distance from center to the outer most region.Atomic properties show pattern amongst the period table which can be classified as trends 6 trends need to know: D.7 (HL) Taxol – a chiral auxiliary case studyĮlectron configuration help determine atomic properties.D.6 Environmental impact of some medications.D.1 Pharmaceutical products and drug action.C.8 Photovoltaic and dye-sensitized solar cells.C.6 Electrochemistry, rechargeable batteries and fuel cells.C.5 Environmental impact – global warming.A.10 Environmental impact – heavy metals.A.8 Superconducting metals and X-ray crystallography.
A.2 Metals and inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectroscopy.21.1 Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds.18.2 Calculations involving acids and bases.16.1 Rate expression and reaction mechanism.14.1 Covalent bonding and electron domain and molecular geometrics.The periodic table – the transition metals 11.3 Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds.11.1 Uncertainties and errors in measurements and results.6.1 Collision theory and rates of reaction.1.1 Introduction to the particulate nature of matter and chemical change.Radius is the size of an atom’s electron cloud and it increases going down and to the left on the periodic table. Acidity increases going down and to the right on the periodic table.Īnd finally we have R which is Radius. This is the ability of a molecule to donate protons and solution. Next we have A, which stands for Acidity. Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom.

All of these E’s increase going up and to the right of the periodic table.Įlectronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself at a covalent bond.Įlectron affinity is the energy associated when you add an electron to an atom.

As you can see, basicity increases going up and to the left of the periodic table.Į stands for three things: Electronegativity, Electron affinity, and ionization Energy. B stands for basicity, the ability of molecules to accept protons. The mnemonic is bear: B E A R.Īnd each letter stands for different chemical properties.
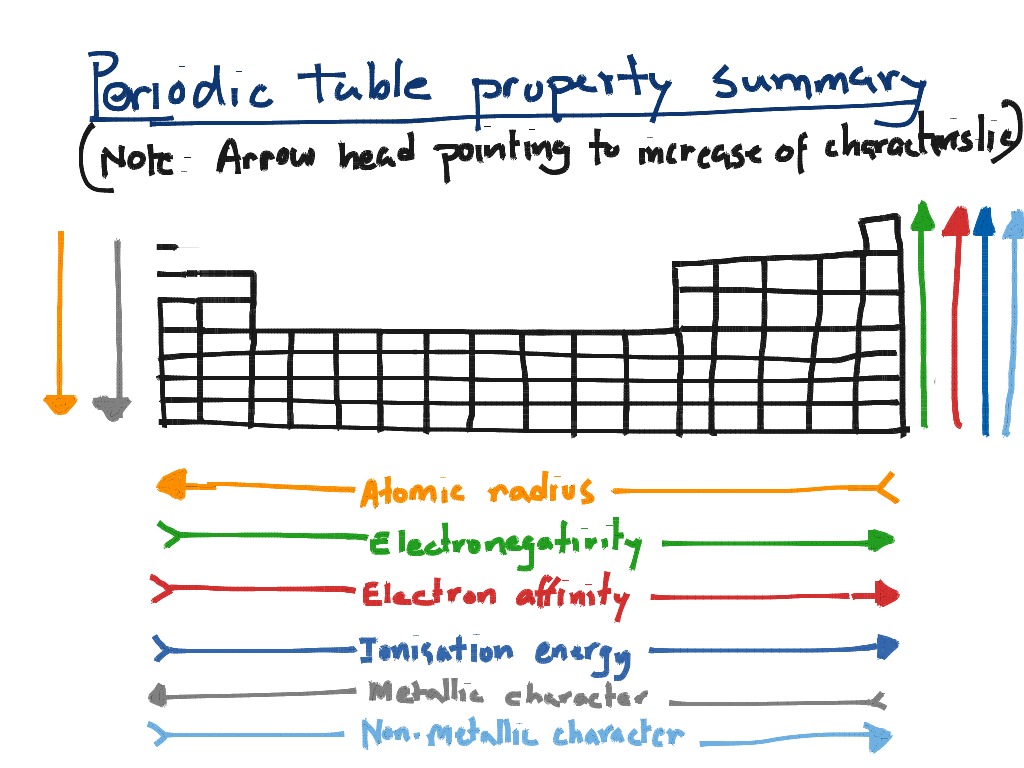
The periodic trends tell you in which direction of the periodic table do you have increasing values for different chemical properties. Today we have another general chemistry mnemonic for you and that mnemonic is for periodic trends. I’m Ken and I’m an MCAT expert with MedSchoolCoach. Welcome back to another MCAT Mnemonic Monday. Ken Tao is the MedSchoolCoach expert on MCAT, and uses the acronym “BEAR” to help you remember the periodic trends for basicity, electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy, acidity and radius.Īll right.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
